Steps how to do the Active Directory migration from
Windows 2008 R2 to Windows 2012 R2.
AD migration from Windows 2008 R2 to Windows 2012 R2.
The steps for the migration are
as follows :
Prerequisites
1.
Download Windows Server 2012 R2. You also have the ability to complete this
Step-By-Step in a virtual lab by downloading Hyper-V Server 2012 for free.
2.
As a precaution, complete a full backup of your existing server.
3.
Check the Schema version of AD DS (Before adprep) by running regedit,
navigating to
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\NTDS\Parameters
and noting the current Schema version.
Step 1: Preparing your
existing forest via the adprep command
1.
Insert the Windows Server 2012 DVD into the DVD drive of the Windows Server
2008 R2 AD DS.
2.
Open command prompt, and type adprep /forestprep and press enter.
3.
Check the Schema version of AD DS (After adprep) by running regedit, navigating
to
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\NTDS\Parameters
and noting the current Schema version.
Step 2: Promoting the Windows
Server 2012 Server domain controller
Prerequisites
1.
Download Windows Server 2012 R2.
2.
Check to ensure the Domain Functional Level is currently setup to at least
Windows 2003 mode. This is the lowest required Domain Functional Level that
would allow a Windows Server 2012 Domain Controller installation. Windows NT /
2000 Domain Controllers are not supported via this process.
1.
Via the Active Directory Users and Computers console, select the domain
via the right mouse button on it.
2.
Select Raise Domain Functional Level and review the Current domain
functional level reported
The Domain Functional Level does
not need to be raised if the Current domain functional level is reporting Windows
Server 2003.
NOTE: Should a lower domain be showcased (i.e., Windows
Server 2000), please keep in mind that raising Domain Functional Level is a one
time action and cannot be reverted. Remember Windows NT / 2000 Domain
Controllers are not supported via this process.
3.
Ensure your profile is a member of the Enterprise Admins group.
Getting Started
1.
Setup and install your Windows Server 2012 machine
2.
Configure the new server's IP address to correspond to the target domain and
ensure the existing Domain Controllers, where DNS is installed and configured,
are visible by your new Windows Server 2012 install.
Setting Up Domain Controller
Functionality
1.
Open the Server Manager console and click on Add roles and features
2.
Select Role-based of featured-based installation and select Next.
3.
Select the Active Directory Directory Services role.
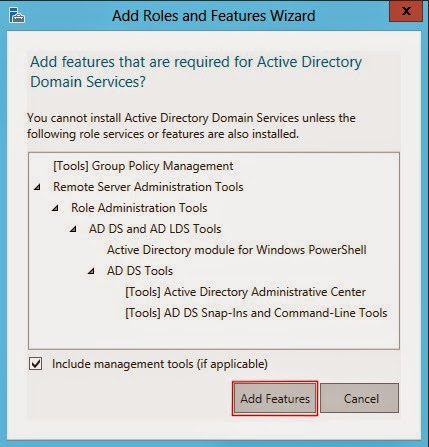
4.
Accept the default features required by clicking the Add Features
button.
5.
On the Features screen click the Next button.
6.
On the Confirm installation selections screen click the Install
button.
NOTE: Check off the Restart the destination
server automatically if required box to expedite
the install should you be able to reset the target server automatically.
7.
Click the Close button once the installation has been completed.
8.
Once completed, notification is made available on the dashboard highlighted by
an exclamation mark. Select it and amidst the drop down menu select Promote
this server to a domain controller.
9.
Select add a Domain Controller into existing domain
10.
Ensure the target domain is specified. If it is not, please either Select
the proper domain or enter the proper domain in the field provided.
11.
Click Change, provide the required Enterprise Administrator credentials
and click the Next button.
12.
Define if server should be a Domain Name System DNS server and Global
Catalog (GC). Select the Site to which this DC belongs to and define Directory
Services Restoration Mode (DSRM) password for this DC
13.
Click the Next button on the DNS options screen.
14.
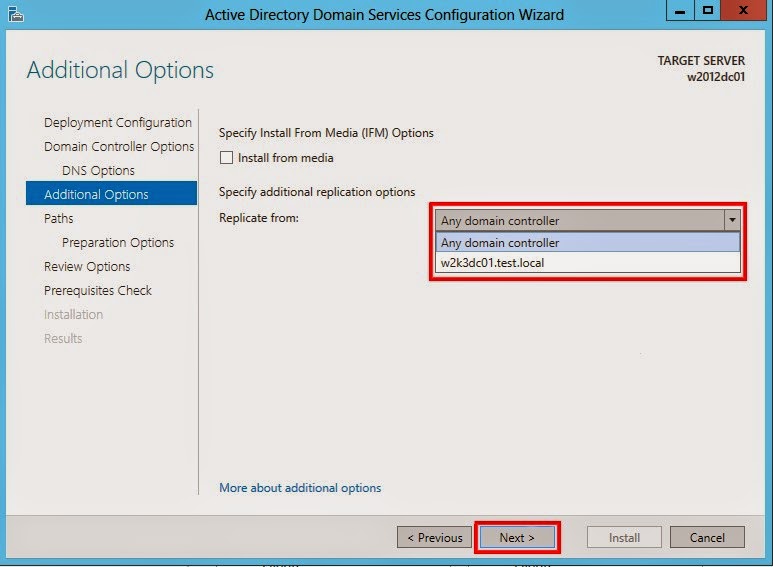
In the Additional Options screen you are provided with the option
to install the Domain Controller from Install From Media
(IFM). Additionally you are provided the option to select the point from which
DC replication should be completed. The server will choose the best location
for AD database replication if not specified. Click the Next button once
completed.
15.
Specify location for AD database and SYSVOL and Click the Next button.
16.
Next up is the Schema and Domain preparation. Alternately, one could run
Adprep prior to commencing these steps, Regardless, if Adprep is not detected,
it will automatically be completed on your behalf.
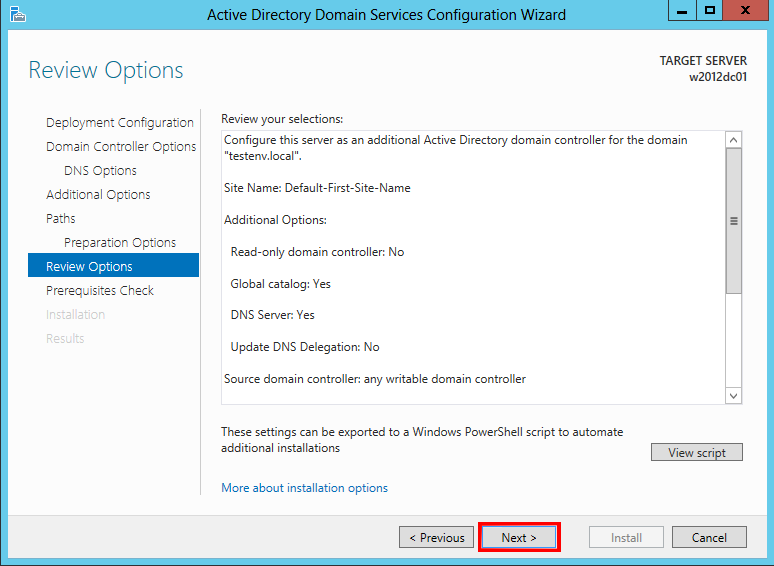
17.
Finally, the Review Options screen provides a summary of all of
the selected options for server promotion. As an added bonus, when clicking View
Script button you are provided with the PowerShell script to automate
future installations. To click the Next button to continue.
18.
Should all the prerequisites pass, click the Install button to start the
installation.
19.
After it completes the required tasks and the server restarts, the new Windows
Server 2012 Domain Controller setup is completed.
20.
Lastly, on each server/workstation within the target domain require a NIC
properties configuration update to point to the new Domain Controller. Open the
DHCP management console, select Option no. 006 and under
server/scope options and add the IP address of your new Domain Controller as
DNS server.
Step 3: Verify the new
Windows Server 2012 Domain Controller
1.
Open Active Directory Users and Computers, expand
and click the Domain Controller OU to verify your server is listed.
2.
Open DNS Manager, right-click on , select Properties
and then click Name ServersTab. Verify that your server
is listed in Name Servers: lists.
3.
Open Active Directory Sites and Services; verify that your server is
listed in Servers under Default-First-Site-Name.
Step 4: Transferring the
Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) Role
1.
Open the Active Directory Users and Computers console on your new
Windows Server 2012 computer.
2.
Right click your domain and select Operations Masters in the sub menu.
3.
In the Operations Masters window, ensure the RID tab is selected.
4.
Select the Change button.
5.
Select Yes when asked about transferring the operations master role.
6.
Once the operations master role has successfully transferred, click OK
to continue.
7.
Ensure the Operations Master box now shows your new 2012 Windows Server.
8.
Repeat steps 4 to 6 for the PDC and Infrastructure tabs.
9.
Once completed, click Close to close the Operations Masters
window.
10.
Close the Active Directory Users and Computers
window.
Step 5: Removing the Windows
2008 R2 domain controller
1.
On the Windows 2008 R2 server click Start, Click Run, type dcpromo,
then click OK.
2.
After the Welcome to the Active Directory Installation Wizard page, be
sure to leave the Delete the domain because this server is the last domain
controller in the domain unchecked.
3.
On the Administrator Password Page, enter your password
and click Next.
4.
On the Summary page, click Next, wait for the process to end,
then click Finish.
5.
On the Completing the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard,
click Finish.
6.
On the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard page, click Restart
Now to Restart the server.
7.
After the reboot is completed, delete the Windows Server 2008 R2 server
from the domain to a workgroup and remove any unnecessary record from Active
Directory Sites and Services.
SCCM
MCP | MCTS | MCSA| MCITP | CNA-Netasq | CCNA | ITIL